You might think that gluten is harmless but for some people it can trigger chronic health issues. It can go unnoticed if you don’t notice the warning signs but over time it can lead to lasting damage. In order to protect your health, you must understand your body’s response to gluten.
1. Gastrointestinal Issues

The symptoms include nausea, bloating, diarrhea, constipation and abdominal pain. People often confuse these signs with other conditions such as Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS). About 10-15% of global population suffers from IBS according to research. This kind of misdiagnosis can prevent people who have gluten sensitivity from receiving the treatment that they require.
2. Change in Weight for No Reason

Your weight can fluctuate due to Gluten intolerance. There will either an increase or a decrease in your weight without any proper explanation. This symptom happens because of disruptions in metabolism and inflammation at the cellular level. Numerous health problems may cause sudden changes in weight but they might indicate gluten intolerance if paired with malabsoption’s other symptoms.
3. Hormonal Imbalance Issues
There are close links between gluten intolerance and sleep disturbances, PMS, unexpected weight changes, and hormonal imbalances manifesting as irregular menstrual cycles. These symptoms are majorly observed in women and are more apparent during pregnancy, puberty and menopause.
4. Problems with Central Nervous System

Gluten has been associated with heightened inflammation and increased intestinal permeability, which can result in various neurological and psychological manifestations. These symptoms may encompass challenges in concentration, depression, anxiety, insomnia, fatigue, irritability, and a phenomenon often referred to as “brain fog,” where individuals find it difficult to sustain focus or clarity of thought.
Furthermore, studies suggest that individuals with gluten intolerance are at a greater risk of experiencing migraines than those without such sensitivity. Although headaches can arise from multiple sources, individuals with gluten sensitivity may observe the onset of a headache within 30 to 60 minutes following the consumption of gluten-containing foods.
5. Skin and Nails Problems

Gluten intolerance is significantly associated with various skin disorders, such as keratosis pilaris and herpetiform dermatitis. Individuals may experience symptoms that present as itchy rashes, which can occur on the hands, torso, face, buttocks, elbows, or around the hairline. Furthermore, gluten sensitivity may contribute to the development of weak, brittle nails and other skin irritations that resemble eczema, potentially arising from gluten-related obstructions within the body.
6. ADHD
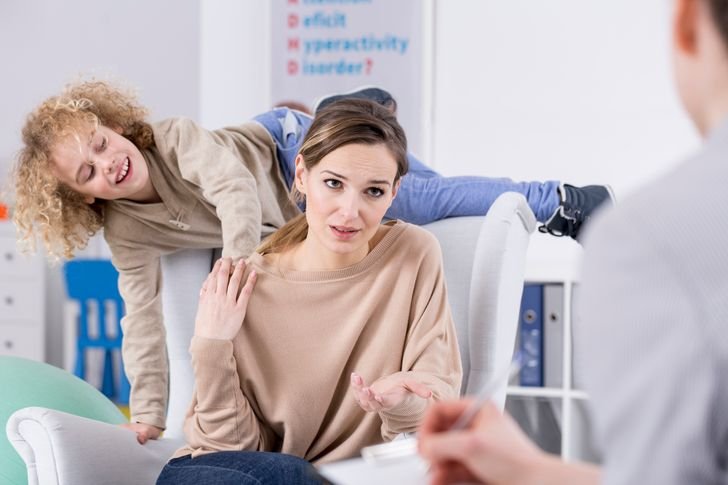

Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a condition that may be associated with gluten intolerance. This disorder impacts individuals of all ages, manifesting as a limited attention span and challenges in self-regulation. Recent studies indicate that implementing a gluten-free diet could potentially reduce certain symptoms related to ADHD.
7. Poor condition of the teeth
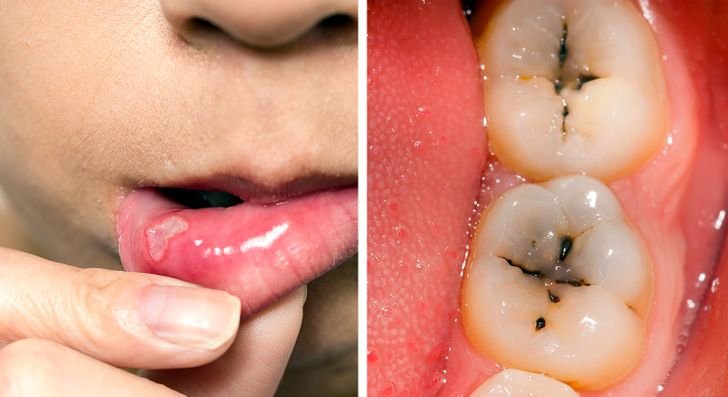
Gluten intolerance can interfere with the absorption of vital nutrients and minerals in the intestines, particularly calcium. This deficiency may result in a range of dental and oral health complications, including enamel sensitivity, tooth decay, cavities, and mouth ulcers. If you practice proper oral hygiene yet still encounter these issues, gluten intake could be the root cause.
8. Iron Deficiency Anemia
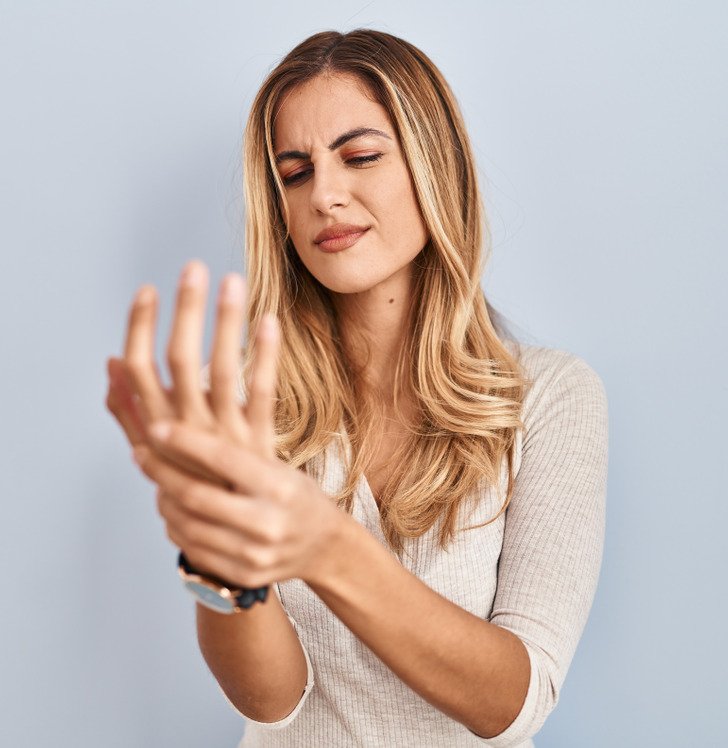

Celiac disease is often identified as a result of iron deficiency anemia, a condition characterized by an insufficient level of iron in the body. The symptoms associated with this type of anemia encompass fatigue, shortness of breath, headaches, and pallor of the skin and mucous membranes, as well as potential joint inflammation. This situation arises because gluten intolerance hinders the intestine’s capacity to effectively absorb iron, resulting in deficiencies even when dietary iron is consumed adequately.
9. Autoimmune Disease
Numerous individuals diagnosed with autoimmune diseases often exhibit a background of gluten intolerance. Celiac disease, classified as an autoimmune disorder, arises when the immune system erroneously targets the intestinal cells following the consumption of gluten. This situation is further complicated by the association of celiac disease with an elevated risk of developing additional autoimmune disorders, such as autoimmune thyroiditis, autoimmune liver disease, Crohn’s disease, diabetes, vitiligo, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis.
10. Tonsil Stones
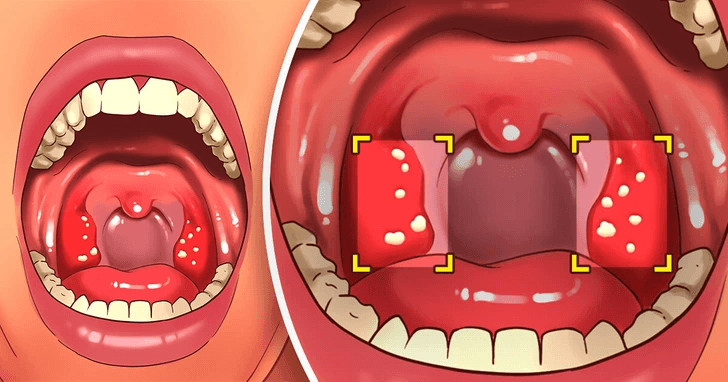
In my clinical experience, while the subject has not been thoroughly researched, it is common to observe tonsil stones in individuals who exhibit gluten sensitivity. Numerous patients have indicated that their tonsil stones tend to diminish following the implementation of a gluten-free diet, implying a possible connection between these conditions.
What’s the treatment for gluten sensitivity?

1. Get Diagnosed:
Consult your physician to undergo a blood test that detects antibodies commonly present in the blood of those diagnosed with Celiac disease. To guarantee precise results, it is essential to maintain gluten in your diet prior to the test.
2. Get on a gluten-free diet
Try to avoid any meals that contains:
- Wheat
- Rye
- Bulgur
- Flour
- Semolina
- And anything else that contains gluten
Whenever you buy grocery, read the labels carefully and if possible buy foods that are clearly marked as “gluten-free”
Always read product labels carefully, and opt for foods marked as “gluten-free” when possible.







